Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (51): 8330-8336.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.51.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of patellar maltracking after arthroscopic lateral retinacular release
Zhang Jian-bing, Hao Jian-qiao, Shen Yun-long, Wang He-wei, Xue Yong-an, Liu Bin
- Department of Orthopaedics, Wenan Hospital, Wenan 065800, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2014-12-10Published:2014-12-10 -
Contact:Zhang Jian-bing, Department of Orthopaedics, Wenan Hospital, Wenan 065800, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jian-bing, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopaedics, Wenan Hospital, Wenan 065800, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jian-bing, Hao Jian-qiao, Shen Yun-long, Wang He-wei, Xue Yong-an, Liu Bin. Analysis of patellar maltracking after arthroscopic lateral retinacular release[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(51): 8330-8336.
share this article
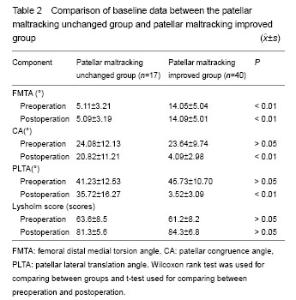
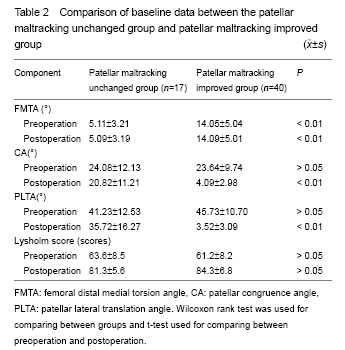
Quantitative analysis of participants Altogether, 43 cases met the inclusion, but 6 patients with external rotation of the femur were excluded. Three patients were lost to follow-up evaluation. At last, 34 patients (57 knees) were enrolled in the study. These 34 patients (57 knees) were located and the study was completed via follow-up. The mean follow-up was (48.0±9.5) months (ranging 9-65 months), while the medical history range was from 1.0 to 5.5 years. Of the 57 knees (34 cases), 45 (78%) were from female patients and 12 (21%) from male patients. Baseline comparison Patellar maltracking unchanged group and patellar maltracking improved group were compared in baseline (Table 2). "
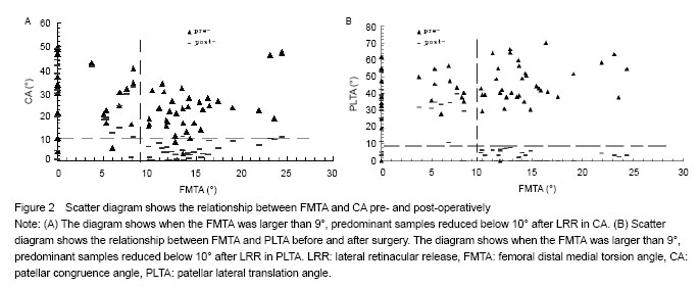
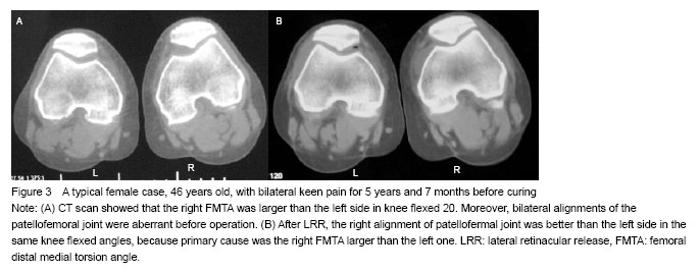
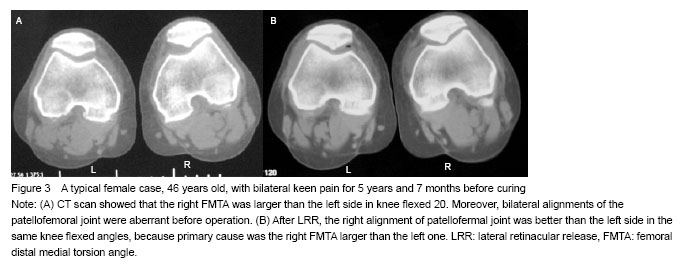
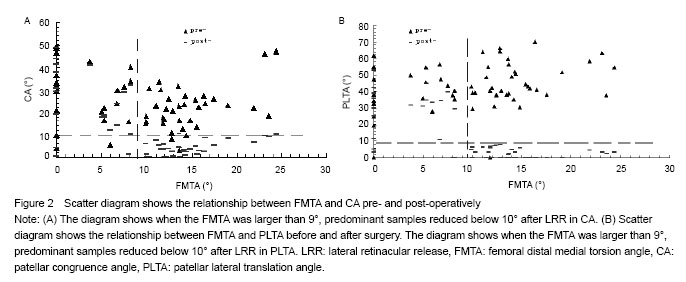
Variation of patellar tracking after arthroscopic lateral retinacular release According to previously published research[8] and our experience, abnormal CA and PLTA values should be improved to nearly normal values (CA: -6°-6°, PLTA: 0°-5°) after LRR. Mean preoperative CA and PLTA values were (23.86±11.39)° and (43.59±10.88)° for 10° of knee flexion, (23.97±11.56)° and (43.70±11.67)° for 20° of knee flexion, (24.10±11.49)° and (43.73±11.53)° for 30° of knee flexion, and (23.51±11.91)° and (43.27±12.13)° for 40° of knee flexion, respectively. The overall mean preoperative FMTA was (10.14±6.45)°, which did not change markedly during the four knee flexion phases. Mean postoperative CA and PLTA values were (11.53± 9.12)° and (12.73± 10.63)° for 10° of knee flexion, (11.67±8.93)° and (12.85± 11.19)° for 20° of knee flexion, (11.97±9.31)° and (12.54± 10.19)° for 30° of knee flexion, and (10.97±8.45)° and (11.09±11.10)° for 40° of knee flexion, respectively. The mean postoperative FMTA was (10.14±6.45)°. Mean FMTA remained unchanged after LRR, regardless of the knee flexion phase. There were 17 knees in which patellar tracking (as indicated by CA and PLTA values) did not improve after surgery and 40 knees in which patellar tracking improved after surgery. The quasi constant FMTA was further examined by comparison between the patellar maltracking unchanged group and patellar maltracking improved group using the Wilcoxon rank test (P > 0.05). Lysholm scores were not different between the two groups before and after LRR, nor were CA and PLTA values before LRR. After LRR, CA and PLTA values were significantly lower in the patellar maltracking changed group compared to the patellar maltracking unchanged group (P < 0.01; Table 1). As shown in Figure 2, FMTA influenced patellar-maltracking recovery after LRR. When FMTA was less than 9° or greater than 9°, postoperative CA and PLTA values were significantly different from preoperative values. Patellar tracking improvement did not meet preoperative expectations when the FMTA was less than 9°. Otherwise, we gathered from some patients that bilateral femoral distal ends presented a different extent of torsion, whose side of the larger FMTA had a better patellar tracking recovery than the lesser side (Figure 3). The evidence also substantiated the findings of the research. "
| [1]Di Giulio M, Donaldson WR. Complications of patello-femoral joint surgery. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2004;12:172-184. [2]Fulkerson JP. Operative management of patellofemoral pain. Ann Chir Gynaecol 1991;80:224-229. [3]Fulkerson JP. Diagnosis and treatment of patients with patellofemoral pain. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30:447-456. [4]Myers P, Williams A, Dodds R, et al. The three in one proximal and distal softt issue patella realignment procedure. Results and its place in the management of patellafemoral instability. Am J Sports Med. 1999;27:575-579. [5]Clifton R, Ng CY, Nutton RW. What is the role of lateral retinacular release? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(1):1-6. [6]Scuderi G, Cuomo F, Scott WN. Lateral release and proximal realignment for patellar subluxation and dislocation. A long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988;70:856-861. [7]Vahasarja V, Kinnunen P, Serlo W. Lateral release and proximal realignment for patellofemoral malalignment. A prospective study of 40 knees in 36 adolescents followed for 1-8 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998;69:159-162. [8]Kolowich P, Paulos L, Rosenberg T, et al. Lateral release of the patella: indications and contraindications. Am J Sports Med. 1990;18:359-365. [9]Ford D, Post W. Open or arthroscopic lateral release. Indications, techniques, and rehabilitation. Clin Sports Med. 1997;16:29-49. [10]Fulkerson JP, Schcutzer SF, Ramsby GR, et al. Computerized tomography of the patellofemoral joint before and after lateral release or realignment. Arthroscopy. 1987; 3: 19-24. [11]Handy M, Miller M. Surgical treatment of acute patellar dislocation. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2001;9:164-168. [12]Farr J. Distal realignment for recurrent patellar instability. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2001;9:176-182. [13]Ahmad C, Stein B, Matuz D, et al. Immediate surgical repair of the medial patellar stabilizers for acute patellar dislocation. A review of eight cases. Am J Sports Med. 2000; 28:804-810. [14]Bigos S, McBride G. The isolated lateral retinacular release in the treatment of patellofemoral disorders. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;186:75-80. [15]Dzioba R. Diagnostic arthroscopy and longitudinal open lateral release. A four year follow-up study to determine predictors of surgical outcome. Am J Sports Med. 1990;18: 343-348. [16]Gerbino PG, Zurakowski D, Soto R, et al. Long-term functional outcome after lateral patellar retinacular release in adolescents: an observational cohort study with minimum 5-year follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28(1):118-123. [17]Harrison RK, Magnussen RA, Flanigan DC. Avoiding complications in patellofemoral surgery. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2013;21(2):121-128. [18]Dandy D, Desai S. The results of arthroscopic lateral release of the extensor mechanism for recurrent dislocation of the patella after 8 years. Arthroscopy. 1994;10:540-545. [19]Christoforakis J, Bull AM, Strachan RK, et al. Effects of lateral retinacular release on the lateral stability of the patella. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14: 273-277. [20]Lee CH, Wu CC, Pan RY, et al. Medial retinacular flap advancement and arthroscopic lateral release for symptomatic chronic patellar lateral subluxation with tilting. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(10):2499-2504. [21]Zaffagnini S, Colle F, Lopomo N, et al. The influence of medial patellofemoral ligament on patellofemoral joint kinematics and patellar stability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(9):2164-2171. [22]Duchman KR, DeVries NA, McCarthy MA, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Iowa Orthop J. 2013;33:64-69. [23]Fulkerson JP. Diagnosis and treatment of patients with patellofemoral pain. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(3):447-456. [24]McCarthy MM, Strickland SM. Patellofemoral pain: an update on diagnostic and treatment options.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2013;6(2):188-194. [25]Schepsis AA, Watson FJ. Patellofemoral Arthritis with Malalignment. Common Patellofemoral Problems. Rosemont, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2005. [26]Sheehan FT, Derasari A, Brindle TJ, et al. Understanding patellofemoral pain with maltracking in the presence of joint laxity: complete 3D in vivo patellofemoral and tibiofemoral kinematics. J Orthop Res. 2009;27:561-570. [27]Wilson NA, Press JM, Koh JL, et al. In vivo noninvasive evaluation of abnormal patellar tracking during squatting in patients with patellofemoral pain. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:558-566. [28]State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01. [29]Nomura E, Inoue M. Cartilage lesions of the patella in recurrent patellar dislocation. Am J Sports Med. 2004; 32:498-502. [30]Simpson LA, Barrett JP Jr. Factors associated with poor results following arthroscopic subcutaneous lateral retinacular release. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;186: 165-171. [31]Dzioba RB. Diagnostic arthroscopy and longitudinal open lateral release. A four year follow-up study to determine predictors of surgical outcome. Am J Sports Med. 1990;18: 343-348. [32]Panni AS, Tartarone M, Patricola A, et al. Long-term results of lateral retinacular release. Arthroscopy. 2005;21: 526-531. [33]Marx RG, Jones EC, Allen AA, et al. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness off our knee outcome scales fo rathletic patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 2001;83A:1459-1469. [34]Pal S, Besier TF, Draper CE, Patellar tilt correlates with vastus lateralis:vastus medialis activation ratio in maltracking patellofemoral pain patients. J Orthop Res. 2012; 30(6):927-933. [35]Lin F, Wilson NA, Makhsous M, et al. In vivo patellar tracking induced by individual quadriceps components in individuals with patellofemoral pain. J Biomech. 2010; 43(2): 235-243. [36]McNally EG. Imaging assessment of anterior knee pain and patellar maltracking. Skeletal Radiol. 2001;30:484-495. [37]Lee TQ, Anzel SH, Bennett KA, et al. The influence of fixed rotational deformities of the femur on the patellofemoral contact pressures in human cadaver knees. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;302:69-74. [38]Besier TF, Gold GE, Delp SL, et al. The influence of femoral internal and external rotation on cartilage stresses within the patellofemoral joint. J Orthop Res. 2008;26:1627-1635. [39]Katchburian MV, Bull AM, Shih YF, et al. Measurement of patellar tracking: assessment and analysis of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;412:241-259. [40]Elkousy H. Complications in brief: Arthroscopic lateral release. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(10):2949-2953. [41]Koh JL, Stewart C. Patellar instability. Clin Sports Med. 2014;33(3):461-76. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [5] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [6] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [7] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [9] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [10] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [11] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [12] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [13] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [14] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [15] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||